Herbal medicine, a timeless practice, harnesses the therapeutic potential of plants to promote health and well-being․ Rooted in tradition, it offers natural remedies for various ailments, emphasizing holistic healing and prevention․ By utilizing botanicals, herbal medicine provides accessible, cost-effective solutions, fostering a deep connection with nature and empowering individuals to take charge of their health naturally․

History and Evolution of Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine traces its roots to ancient civilizations, where plants were first used for healing and spiritual practices․ Early cultures in China, India, Egypt, and Greece documented the medicinal properties of herbs, laying the foundation for traditional systems of health care․ Over centuries, herbalism evolved through empirical observation and cultural exchange, with remedies being passed down through generations․ The Middle Ages saw the rise of monasteries as centers for herbal knowledge preservation․ By the Renaissance, herbalism became more systematic, with the development of pharmacopoeias․ The 19th and 20th centuries marked a shift toward modern medicine, but herbal practices persisted, blending with scientific advancements․ Today, herbal medicine is recognized globally, integrating traditional wisdom with evidence-based research to create safe, effective remedies for modern health challenges․

Materials and Equipment Needed for Herbal Medicine Preparation
Essential materials include dried or fresh herbs, mason jars, dark glass bottles, and a mortar and pestle․ Key equipment for preparation involves strainers, cheesecloth, and measuring tools for precise dosing․
3․1․ Harvesting Herbs: Best Practices
Harvesting herbs requires careful timing and technique to ensure optimal potency and quality․ For most herbs, the ideal time to harvest is during the early morning, after the dew has evaporated but before the heat of the day․ This ensures the highest concentration of essential oils and active compounds․ Use sharp, clean tools like scissors or pruning shears to avoid damaging the plants․ Harvest leaves and flowers when they are at their peak freshness and color․ Roots and rhizomes are typically harvested in the fall or early spring when the plant’s energy is concentrated underground․ Proper identification of the plant is crucial to avoid mistakenly harvesting toxic species․ Always harvest in a sustainable manner, leaving enough of the plant to ensure regrowth and maintain ecological balance․ This approach respects both the plant and the environment, ensuring a bountiful supply for future use․

Herbal Medicine Preparation Methods
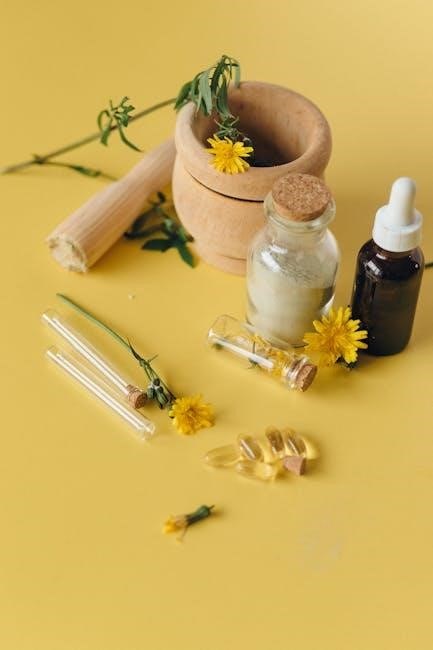

Herbal medicine preparation involves infusions, decoctions, tinctures, and extracts, using water, alcohol, or glycerin as solvents․ These methods unlock herbs’ active compounds, ensuring effective and natural remedies․
4․1․ Preparing Herbal Infusions
Herbal infusions are a simple and effective way to enjoy the benefits of herbs․ Start by measuring 1 teaspoon of dried herbs or 2 teaspoons of fresh herbs for every 8 ounces of boiling water․ Pour the water over the herbs in a teapot or heat-resistant cup, then cover to steep for 5-15 minutes, depending on the herb’s potency․ Strain the mixture into another container using a fine-mesh sieve or cheesecloth to remove the solids․ Infusions can be consumed hot or iced, sweetened with honey, or enhanced with lemon juice for flavor․ For best results, use high-quality, organic herbs and store any leftovers in the refrigerator for up to 24 hours․ Always consult a healthcare provider before using herbal remedies, especially if you have a medical condition or are taking medications․
4․2․ Creating Decoctions
A decoction is a concentrated herbal preparation made by boiling tougher plant materials like roots, bark, and seeds․ To create a decoction, combine 1 tablespoon of dried herbs or 2 tablespoons of fresh herbs with 12 ounces of water in a pot․ Bring the mixture to a boil, then reduce the heat and simmer for 20-40 minutes, allowing the flavors and active compounds to extract․ Strain the liquid through a fine-mesh sieve or cheesecloth into a clean container․ Decoctions can be consumed warm or cooled, and they are often used as a base for teas, soups, or other remedies․ For optimal potency, store decoctions in the refrigerator for up to 48 hours․ Reusable herbs can be steeped multiple times until their flavor and effectiveness diminish․ This method is particularly effective for extracting nutrients from hardy plant parts․
4․3․ Making Tinctures and Extracts
Tinctures and extracts are concentrated forms of herbal medicine, offering potent and convenient solutions for health․ To make a tincture, combine 1 part dried herb with 5 parts alcohol (typically 80-100 proof) or 1 part fresh herb with 2 parts alcohol in a clean glass jar․ Store the mixture in a cool, dark place for 2-6 weeks, shaking daily to extract the herbal compounds․ After steeping, strain the liquid through cheesecloth or a fine-mesh sieve into a dark glass bottle․ Tinctures are usually taken sublingually in small doses (20-30 drops)․ Extracts, often made similarly but with glycerin instead of alcohol, are a sweeter alternative․ Both tinctures and extracts are shelf-stable for years, making them a versatile option for long-term herbal remedies․ Always label and store them properly to maintain potency and safety․
Safety Considerations and Precautions
When preparing herbal remedies, safety is paramount to ensure effectiveness and avoid adverse effects․ Always consult a healthcare professional before using herbal medicine, especially if pregnant, breastfeeding, or on prescribed medications․ Correctly identify plants to avoid accidental toxicity․ Start with small doses to test for allergies or sensitivities․ Be aware of potential interactions between herbs and medications․ Use high-quality, organic ingredients free from contaminants․ Follow trusted recipes and guidelines for preparation to maintain safety and potency․ Keep herbal remedies out of reach of children and pets․ Store them in labeled, airtight containers away from heat, light, and moisture․ Avoid overconsumption, as even natural remedies can cause harm in excess․ Research the specific contraindications for each herb to ensure safe use․ By adhering to these precautions, herbal medicine can be a safe and effective natural health solution․

Proper Storage of Herbal Remedies
Proper storage is essential to maintain the potency and shelf life of herbal remedies․ Store herbal preparations in a cool, dark, and dry place to protect them from heat, light, and moisture․ Use airtight containers such as mason jars with tight-fitting lids or dark glass bottles to prevent exposure to air and light․ Label each container with the herb’s name and preparation date for easy identification․ Avoid storing herbs in humid or warm areas, such as kitchens or bathrooms, as moisture and heat can degrade the remedies․ For liquid-based remedies like tinctures, store them in dark glass bottles and consider keeping them in the refrigerator to slow oxidation․ Regularly check stored herbs for signs of spoilage or degradation․ Proper storage ensures the longevity and effectiveness of your herbal remedies, allowing you to enjoy their benefits for months to come․

Popular Herbal Remedies and Recipes
Herbal remedies offer a wide range of natural solutions for common ailments․ One popular remedy is calendula salve, made from calendula flowers, which soothes skin irritations and wounds․ Another is chamomile tea, known for its calming effects and ability to aid sleep․ Elderberry syrup is a favorite for fighting colds and flu, while ginger tea alleviates digestive issues and inflammation․ Many herbalists also swear by echinacea tinctures to boost the immune system․ These remedies can be prepared using simple methods like infusions, decoctions, or macerations․ For example, steeping dried chamomile flowers in hot water creates a soothing infusion, while simmering ginger root makes a potent decoction․ Always use fresh, organic herbs and follow trusted recipes to ensure safety and efficacy․ These natural remedies not only promote health but also connect us to the healing power of plants․
Efficacy and Evidence-Based Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine’s efficacy is increasingly supported by scientific research, bridging traditional practices with modern evidence-based approaches․ Clinical trials have validated the benefits of herbs like St․ John’s Wort for mild depression and Echinacea for immune support․ Studies highlight the importance of bioactive compounds in herbs, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, which contribute to their therapeutic effects․ However, variability in herbal quality and preparation can impact potency․ To ensure safety and effectiveness, standardized extracts and adherence to validated preparation methods are crucial․ Research also emphasizes the need for professional guidance, especially for individuals on prescribed medications․ Evidence-based herbal medicine integrates traditional knowledge with contemporary science, offering reliable natural health solutions while addressing modern health challenges effectively․ Always consult reputable sources, like the American Herbal Pharmacopoeia, for scientifically backed herbal remedies and usage guidelines․ This approach ensures herbal medicine remains a viable, trustworthy option for holistic well-being․
Herbal medicine offers a natural and effective way to promote health and well-being, blending centuries-old traditions with modern scientific understanding․ By harnessing the therapeutic properties of plants, individuals can create remedies that address a variety of health concerns․ The process of making herbal medicine empowers people to take an active role in their health, fostering a deeper connection with nature and holistic wellness․ While herbal remedies can be highly effective, it is essential to approach their preparation and use with care, ensuring proper techniques and safety precautions․ As interest in natural health solutions grows, herbal medicine stands as a timeless and accessible option for those seeking alternatives to conventional treatments․ Always consult reliable resources and professionals to ensure safe and effective use․ By embracing this ancient yet evolving practice, individuals can continue to benefit from the healing power of herbs for generations to come․